

#Ninox swir 640 how to
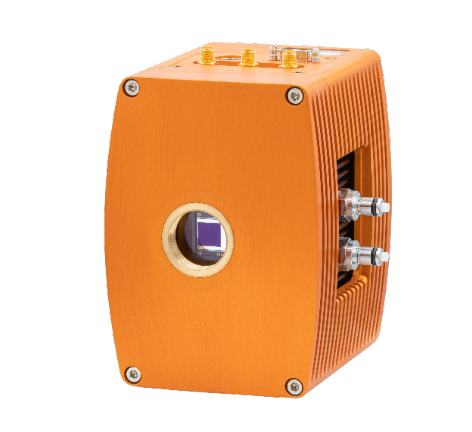
The course addressed how to use CompleteEASE, through a comprehensive introduction, as well as how to model different types of materials (transparent, absorbing, semi-absorbing and ultra-thin films) and how to characterise multiple samples concurrently (model multiple datasets), multi-point data mapping and model dynamic data (time series data).I can confidently recommend this event to anyone seeking to improve their expertise in materials characterisation, in particular spectroscopic ellipsometry. Regarding the training course, it provided step-by-step guidance on how to best leverage spectroscopic ellipsometry for sample characterisation (measurement and analysis), using J.A. The camera has a response in the SWIR region from 0.9m to 1.7m. This definitely provided the necessary background and context for newly acquainted users, as well as serving as a “refresher” for more experienced users. SPECIFICATION 3.1 Camera Overview The Ninox 640 SU is a 16-bit deep cooled SWIR camera.
#Ninox swir 640 software
Woollam CompleteEASE Software Training Course, as a whole, was a very interesting and informative event, engaging its attendees to participate in the discussion of the various seminars and training sessions.įrom the workshop you had an introduction to spectroscopic ellipsometry and its applications, as well as exposure to the latest research in the field, showcasing real-world use cases in advanced characterisation. Woollam Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Workshop and the J.
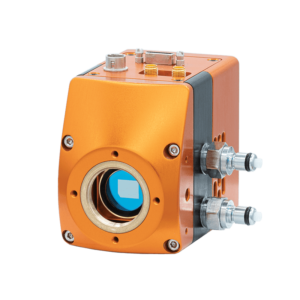
(400- Headquarters: Willowbank Business Park, Larne, Co.Both the J. This paper will be restricted to a discussion of the performance of InGaAs detector arrays, sensitive in the VIS-SWIR region, i.e. The use of imaging systems to capture long wavelength photons (beyond the detection range of Silicon based devices) continues to increase in many diverse application areas, such as life sciences, security & surveillance, non-destructive testing, quality control and astronomy. Figure 1: The typical definition of the various sub-regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, covering visible through to infrared wavelengths. Each of the materials above present their own advantages and challenges and therefore prior to detector selection the user must consider all aspects of the intended application, in addition to simply the wavelength response. The typical definition for each 'sub-region' within VIS-IR wavelength range is outlined in Figure 1.

The materials listed have been developed into detection systems which enable images to be acquired within the various regions of the visible to infrared spectrum. Ninox ULTRA 640 SWIR High resolution, low noise, Deep cooled, digital SWIR camera 640 x 512 Cooled to -80C <30e in high gain Key Features and Benefits The best performing SWIR camera in the World Deep cooled to -80C with PentaVac, Raptor’s Vacuum technology Enables ultra low dark current and longer exposure 15m x 15m. Detector Material Typical VIS-IR Detection Range Indium Gallium Table 1: Common detector materials and their typical detection range within the VIS-IR wavelength Above llOOnm, Silicon is transparent and therefore cannot be used to detect photons of these wavelengths, however many other materials do have photon sensitivity at these wavelengths and longer, see Table 1. The Ninox 640 II is the next generation of the highly successful. Typically the quantum efficiency (QE) of these detectors decreases rapidly as the detection wavelength increases further into the NIR region. High resolution, low noise, digital InGaAs camera. CCDs or CMOS) are widely used in high performance imaging applications, detecting wavelengths from soft x-ray through to near infrared (NIR). High Performance SWIR Imaging Cameras Introduction to SWIR Imaging Silicon based area detectors (e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
